Feature update
Introduction
After the decentralization of the BLOCKv Network in 2020 delivered marked improvements to scalability and partner node autonomy, it's safe to say that 2021 has already seen the BLOCKv ecosystem flex its newfound muscles and step into the metaverse. So far BLOCKv and our partner nodes have used our technical stack to create wearable NFTs, completely web based augmented reality portals and a full scale virtual space hosting platform featuring spatial audio, NFT gift bags and virtual networking capabilities that would make a Zoom conference blush.
In their 2020 report on the future of computing and Web 3.0, Deloitte discuss how industry leaders are increasingly moving away from traditional methods of interacting with data, instead focusing on creating new user interfaces that will emerge from “the growth and convergence of enabling technologies, including augmented and virtual reality, advanced networking [e.g., 5G], geolocation, IoT devices and sensors, distributed ledger technology [e.g., blockchain], and artificial intelligence/machine learning”. The ability to interact with BLOCKv NFTs in spaces like augmented reality and virtual arenas is just one of the ways in which our ecosystem members intend to build and refine these Web 3.0 aligned user interfaces. In this update we’re going to be breaking down not only how these features were technically accomplished, but also how they fit into BLOCKv’s wider role in building the future of the digital metaverse.
The future is augmented - major improvements to how our nfts can be used in augmented reality
A recent surge in news and product launches in the Augmented Reality sector from the likes of Microsoft, Facebook and Snap has put AR firmly back into the public consciousness and we’re excited to show you what we’ve been building in this fast moving space.
Wearable NFTs - not just a pretty face
Perhaps the most exciting feature we’ve developed has been the creation and deployment of wearable NFTs. One of the most popular uses of BLOCKv NFTs has been to create and distribute unique digital objects that users can view and interact with in AR, and wearable NFTs add a fresh new dimension to this user experience. Our development team worked with 8th Wall to combine the unique, interactive nature of our programmable NFTs with the wildly popular ‘face filter’ format - producing wearable NFTs that users can interact with in augmented reality. Whilst wearable face filters have been around for a few years now, wearable NFTs differ from generic filters in a number of ways. Firstly, these wearables are not just a filter, but instead a fully fledged digital object that you can, if you choose to, interact with using your face. BLOCKv’s NFTs can be broadly broken down into 3 distinct parts: the reactor core, its user interface layer, and the behaviour it can undertake. Each part of the structure serves a different role, and the ability to wear a BLOCKv NFT as a face filter is housed within under the user interface layer, which we call the ‘face’.
Our NFTs can display multiple faces depending on the device or medium upon which it is being viewed. During the face selection config, if programmed, they can intelligently detect which platform they’re being accessed from and call a different face in response to this, meaning it can look and act differently within an IOS, Android, laptop, VR, AR and even IOT environment. In the example below, you can see the different faces of the deal with it sunglasses NFT in action. Each of these ‘faces’ is the same unique digital object, being visually represented in a number of different ways within different spaces. Much cool, very wow.
Wallet Card - a static card that informs the user of how the NFT works, what functions it can perform and provides them with various input options.
3D model viewer - An optional interactive 3D model of the sunglasses that is displayed behind the wallet card.
Wearable face filter - an interactive 3D model that can be worn by the user in augmented reality through face tracking.
The wearable NFT feature has already been used in two major projects this year, a commercial campaign for Because Creative Experiences and as a fun extra for the Million Doge Disco, and we’re excited to work more with it in the future! If we move from form to function, this new method of interacting with NFTs brings with it a host of new opportunities for recording and actioning user input. By combining BLOCKv’s pre-existing transactional ledger capabilities (which record all user interactions) with face tracking technology, it is now possible to interact with, and by extension make permanent changes to, digital objects from within augmented reality.
Augmented reality portals - a potential future partnership with Aperture Science?
The BLOCKv development team and our partners have also been working on creating augmented reality portals that are accessible from within our web viewer. These ‘portals’ are sent as interactive NFTs to users and upon being deployed in augmented reality become a gateway to an augmented reality experience, displaying a door to a computer generated virtual space that exists within the AR viewer. The portals can be accessed by users straight from their mobile browser with no download or specialist hardware required. Whilst we might have been kidding about the partnership with Aperture, the potential applications of this technology are no joke. From virtual galleries to online shopping spaces, creative developers can add a whole new layer to their digital engagement platforms with these portals. Within the context of digital and experiential marketing, creating novel and memorable user experiences with technology such as augmented reality not only promotes positive brand association by generating entertainment value, it also provides a new means of completely immersing consumers in brand imagery from the comfort of their homes. The success of previous projects utilising augmented reality gamification (such as Ben & Jerry’s Easter Hunt, Vodafone Find Unlimited and Doritos Quest), have shown implementing extended reality gameplay leads to longer dwell times and returning users and we think AR portals are the next step in evolution for this new kind of experiential marketing.
Vatom inc. debut spatial audio and Vatom NFT goodie bags for attendees of Cannes Lions 2021’s virtual networking hub
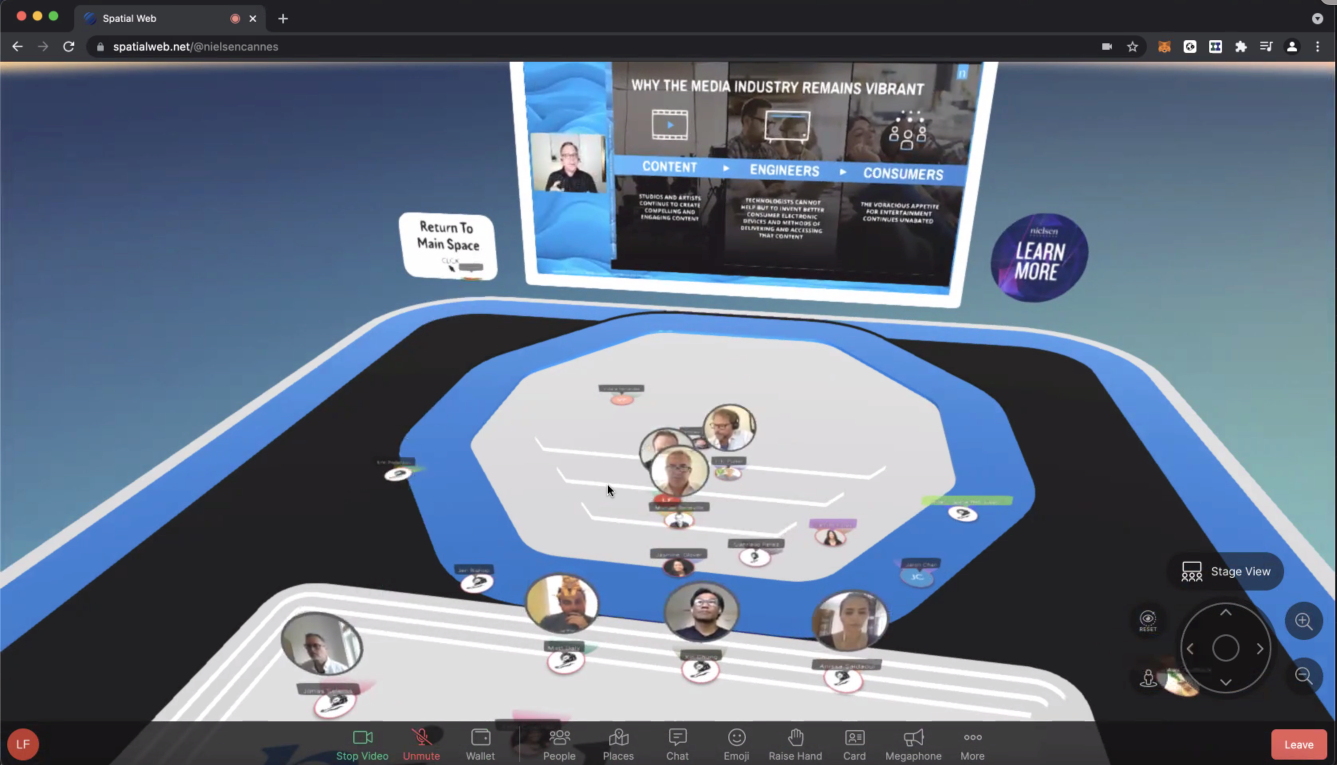
Cannes Lions is one of the highest profile events of the year for the advertising and creative communications industry, with around 15,000 attendees each year coming together to debut, debate and decorate the most innovative media campaigns of the year over five days. It’s also long been a chance to hear from and rub shoulders with some of the keenest minds in the sector, and is therefore a coveted networking opportunity. After 2020’s festival was cancelled due to Covid-19, speculation was rife around how the Lions would recreate its famed atmosphere when travelling across borders was still largely restricted. Enter The Vatom Spatial Web, a web based tool developed by BLOCKv Network node Vatom Inc. that allows anyone to create, host and attend virtual spaces straight from their browser. The Vatom Spatial Web created an exclusive ticketed networking hub for attendees of the festival, with talks on a wide variety of topics being hosted over the course of the festival on multiple virtual stages that attendees could watch and discuss with others in real time, thanks to the inclusion of spatial audio and video chat functionality. One of the most interesting technology use cases to come out of the event was the distribution of NFT powered virtual ‘goodie bags’ to attendees. Whilst in the virtual space, attendees could view, interact with and even drop Vatom Inc. NFTs around them for other attendees to pick up, recreating arguably the best part of any conference (the free gifts) within the metaverse. This use case exemplifies how the decentralised architecture of the BLOCKv Network ensures every partner node operates entirely independently of the others, whilst still benefiting from the implementation of BLOCKv’s technology stack in their services.
Cannes Lions attendees use the Vatom Spatial Web to watch a presentation and discuss with fellow attendees in real time
Web 3.0 and the future of data
We believe the ability to create wearable NFTs and AR portals within the BLOCKv Network ecosystem provides the beginnings of a digital toolkit that will enable developers to build products aligned with Web 3.0 principles. If you’re wondering exactly what Web 3.0 is, it refers to the belief that the next wave of technological innovation will be focused around changing the way we interact with data and digital content from a screen based process to the physical space around us. Whilst Web 3.0 is the most generic term for this broad ranging idea, it’s also been labelled as ‘the Semantic Web’ by Sir Tim Berners Lee and The Spatial Web by Deloitte and others. As part of this evolution, Web 3.0 promises to change not only the way we interact with technology and data, but also the way in which data is processed and information itself is stored. If this all sounds a little to ‘Ready Player One’ to actually be possible, we’ve broken down how we believe our NFTs can enable this. Beyond the slick AR glasses, VR headsets and gesture controllable smart devices lies a new logic of how data is processed and stored. We wanted to build a platform that not only worked well today, but also grew more powerful as other technical services advanced in their functionality in the future. This belief in adaptability and evolution is one of the defining logics behind the creation of the BLOCKv platform, which is why the BLOCKv Network was created to decentralise the process of generating and emitting NFTs and is why our NFTs are not bound to any one chain. The ability to choose from a number of leading blockchains including; Ethereum, Polygon and Binance Smart Chain allows our Network users to benefit from each chain’s unique strengths.
Another necessary step towards completing the integration of the digital and physical worlds, something we call ‘reality synchronization’, is the ability to instantly scale processing power to wherever it is needed. We’ve also designed a data storage path for our NFTs that allows the system to operate with theoretically limitless scalability. If you’re interested in reading more about this check out our previous technical blog for more details and a handy diagram. These features, alongside the private blockchain node we’ll be adding later this year, will all allow us to play our part in developing the infrastructure behind Web 3.0, and help to build a future where Deloitte believes ‘digital information will exist in space, integrated and inseparable from the physical world’.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the past 6 months have brought some great advances in BLOCKv’s technology stack, both in viable industry use cases and in technical showcases for how non-fungible technology could be used in the future. With builds such as a provisioned private blockchain node pencilled in for the last half of the year bringing more options and Web 3.0 aligned functionality to the platform, we’re excited as always to share more of what we’ve been working on with you all soon. If you’d like to learn more about any of the features discussed in this post and how you can use them in your projects ping us an email at info@blockv.io and we’ll be in touch!